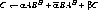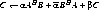|
PROGRAM TEST
|
IMPLICIT NONE
|
C
|
REAL RZERO
|
INTEGER K, LDA, LDB, LDC, N
|
PARAMETER (K = 2)
|
PARAMETER (N = 3)
|
PARAMETER (LDA = N)
|
PARAMETER (LDB = N)
|
PARAMETER (LDC = N)
|
PARAMETER (RZERO = 0.0E0)
|
C
|
COMPLEX A(LDA,K), ALPHA, B(LDB,K), BETA, C(LDC,N)
|
INTEGER I, J
|
C
|
EXTERNAL CHER2K
|
INTRINSIC CMPLX, CONJG, REAL
|
C
|
C Initialize the arrays A and B to store the matrices A and B
|
C shown below. Initialize the array C to store in symmetric
|
C form the Hermitian matrix C shown below.
|
C
|
C 1+1i 1+2i 2+1i 3+2i 4+3i 1+0i 2-3i 4-5i
|
C A = 2+1i 2+2i B = 3+1i 4+2i 5+3i C = 2+3i 6+0i 7-8i
|
C 3+1i 3+2i 4+5i 7+8i 9+0i
|
C
|
DATA A / (1.0,1.0), (2.0,1.0), (3.0,1.0),
|
$ (1.0,2.0), (2.0,2.0), (3.0,2.0) /
|
DATA B / (2.0,1.0), (3.0,1.0), (4.0,1.0), (3.0,2.0),
|
$ (4.0,2.0), (5.0,2.0) /
|
DATA C / (1.0,8E8), (2.0,3.0), (4.0,5.0),
|
$ (8E8,8E8), (6.0,8E8), (7.0,8.0),
|
$ (8E8,8E8), (8E8,8E8), (9.0,8E8) /
|
C
|
ALPHA = CMPLX (1.0E0,0.0E0)
|
BETA = CMPLX (0.0E0,3.0E0)
|
PRINT 1000
|
DO 100, I = 1, N
|
PRINT 1010, (A(I,J), J = 1, K)
|
100 CONTINUE
|
PRINT 1020
|
DO 110, I = 1, N
|
PRINT 1010, (B(J,I), J = 1, K)
|
110 CONTINUE
|
PRINT 1030
|
DO 120, I = 1, N
|
PRINT 1010, (C(I,J), J = 1, I - 1), REAL (C(I,I)), RZERO,
|
$ (CONJG (A(J,I)), J = I + 1, N)
|
120 CONTINUE
|
PRINT 1040
|
DO 130, I = 1, N
|
PRINT 1010, (C(I,J), J = 1, N)
|
130 CONTINUE
|
CALL CHER2K ('LOWER TRIANGULAR C', 'NOT TRANSPOSED C', N, K,
|
$ ALPHA, A, LDA, B, LDB, BETA, C, LDC)
|
PRINT 1050
|
DO 140, I = 1, N
|
PRINT 1010, (C(I,J), J = 1, I), (CONJG (C(J,I)),
|
$ J = I + 1, N)
|
140 CONTINUE
|
PRINT 1060
|
DO 150, I = 1, N
|
PRINT 1010, (C(I,J), J = 1, N)
|
150 CONTINUE
|
C
|
1000 FORMAT (1X, 'A:')
|
1010 FORMAT (3(3X, : '(', F5.1, ',', F5.1, ')'))
|
1020 FORMAT (/1X, 'B:')
|
1030 FORMAT (/1X, 'C in full form:')
|
1040 FORMAT (/1X, 'C in Hermitian form: (* in unused elements)')
|
1050 FORMAT (/1X, 'AB'' + BA'' + C in full form:')
|
1060 FORMAT (/1X, 'AB'' + BA'' + C in Hermitian form:')
|
C
|
END
|
|