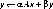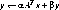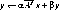|
PROGRAM TEST
|
IMPLICIT NONE
|
C
|
INTEGER LDA, M, N, NSUB, NSUPER
|
PARAMETER (M = 5)
|
PARAMETER (N = 5)
|
PARAMETER (NSUB = 0)
|
PARAMETER (NSUPER = 2)
|
PARAMETER (LDA = NSUB + 1 + NSUPER)
|
C
|
INTEGER I, J
|
DOUBLE PRECISION A(LDA,N), ALPHA, BETA, X(N), Y(N)
|
C
|
EXTERNAL DGBMV
|
INTRINSIC MIN
|
C
|
C Initialize the array A to store in banded form the matrix A
|
C with two superdiagonals and no subdiagonals shown below.
|
C Initialize the arrays X and Y to store the vectors x and y
|
C shown below.
|
C
|
C 1 1 1 1 1
|
C 2 2 2 2 1
|
C A = 3 3 3 x = 3 y = 1
|
C 4 4 4 1
|
C 5 5 1
|
C
|
DATA A / 8.0D8, 8.0D8, 1.0D0, 8.0D8, 1.0D0, 2.0D0,
|
$ 1.0D0, 2.0D0, 3.0D0, 2.0D0, 3.0D0, 4.0D0,
|
$ 3.0D0, 4.0D0, 5.0D0 /
|
DATA X / 1.0D0, 2.0D0, 3.0D0, 4.0D0, 5.0D0 /
|
DATA Y / 1.0D0, 1.0D0, 1.0D0, 1.0D0, 1.0D0 /
|
C
|
PRINT 1000
|
DO 10, I = 1, N
|
PRINT 1010, (0.0D0, J = 1, I - 1),
|
$ (A(3 - J,J + I), J = 0, MIN(5 - I, 2)),
|
$ (0.0D0, J = 1, 3 - I)
|
10 CONTINUE
|
PRINT 1020
|
DO 20, I = 1, 3
|
PRINT 1010, (A(I,J), J = 1, N)
|
20 CONTINUE
|
PRINT 1030
|
PRINT 1040, (X(I), Y(I), I = 1, N)
|
ALPHA = 2.0D0
|
BETA = 3.0D0
|
CALL DGBMV ('NO TRANSPOSE A', M, N, NSUB, NSUPER, ALPHA,
|
$ A, LDA, X, 1, BETA, Y, 1)
|
PRINT 1050
|
PRINT 1060, Y
|
C
|
1000 FORMAT (/1X, 'Array A in full form:')
|
1010 FORMAT (1X, 5(2X, F4.1))
|
1020 FORMAT (/1X, 'Array A in packed form: ',
|
$ ' (* in unused fields)')
|
1030 FORMAT (/5X, 'x', 5X, 'y')
|
1040 FORMAT (3X, F4.1, 2X, F4.1)
|
1050 FORMAT (/1X, 'Ax + y:')
|
1060 FORMAT (3X, F4.1)
|
C
|
END
|
|